- Fabrication of Eco-friendly PLA/PBAT-based Composites Through Conductive Network Formation
Department of Chemical Engineering, Soonchunhyang University, Asan-si, Chungcheongnam-do, 31538, Korea
- 전도성 네트워크 형성을 통한 PLA/PBAT 기반 친환경 복합소재 제조
순천향대학교 공과대학 나노화학공학과
Reproduction, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form of any part of this publication is permitted only by written permission from the Polymer Society of Korea.
Recently, the development of eco-friendly materials has attracted increasing attention as a major solution to reduce environmental pollution. Therefore, if conductive materials are manufactured using biodegradable polymers, eco-friendly conductive composites can be applied in various fields. In general, a large amount of filler is required to achieve conductivity; however, excessive filler loading leads to increased cost and deterioration of mechanical properties. For this reason, it is important to develop materials with high conductivity at low filler contents. In this study, biodegradable conductive composites were fabricated by optimizing conductive network formation, mixing conditions, and polylactic acid (PLA)/polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) compatibility. As a result, the optimal carbon nanotube (CNT) content and processing conditions were determined, and biodegradable polymer composites with high electrical conductivity were obtained using the minimum filler content. Furthermore, the incorporation of a compatibilizer enabled the fabrication of composites with improved mechanical properties. It was also confirmed that, for the formation of a conductive network, the spatial distribution of CNTs and the development of a co-continuous structure play a more critical role than the compatibility enhancement of the immiscible polymer matrix.
최근 환경오염을 줄이기 위해 친환경 소재 개발이 주요 해결책으로 주목받고 있다. 따라서, 생분해성 소재로 전도성 소재를 제작하면 친환경 소재를 다양한 방향으로 사용이 가능할 것이다. 전도성 소재를 제조하기 위해서는 많은 양의 필러 첨가가 필수적인데 과량의 필러는 단가 상승, 기계적 물성 저하를 초래한다. 이러한 이유로 적은 함량으로 높은 전도성을 가지는 소재를 제작하는 것이 중요하다. 본 연구에서는 전도성 네트워크 형성, 혼합 공정 최적화, polylactic acid(PLA)/polybutylene adipate terephthalate(PBAT) 상용성 개선을 통해 생분해가 가능한 친환경 전도성 복합소재를 제조하였다. 그 결과 탄소나노튜브의 함량 및 공정 최적화를 달성하였고, 최소 함량의 필러를 사용하여 높은 전기전도성을 가지는 생분해성 고분자 복합소재를 제조하였다. 특히, 상용화제를 첨가하면 기계적 물성이 우수한 소재를 제조할 수 있었다. 또한, 전도성 네트워크를 형성하기 위해서는 비상용성 폴리머 매트릭스의 상용성 개선보다도 탄소나노튜브의 위치와 공연속 구조 형성이 더 중요한 요소임을 확인하였다.
A biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA)/polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) blend composite achieves high electrical conductivity with minimal carbon nanotube (CNT) content through co-continuous morphology and optimized mixing. The double percolation structure enables efficient conductive network formation, making it suitable for EMI shielding and wearable electronics.
Keywords: biodegradable polymers, conductive polymers, carbon nanotubes, percolation threshold, rheology.
본 연구는 순천향대학교 학술연구비 지원으로 수행하였음.
저자(들)는 이해상충이 없음을 선언합니다.
전 세계적으로 플라스틱 수요가 증가함에 따라 플라스틱 생산 및 폐기물이 급속도로 증가하면서 환경 문제를 야기하고 있다.
플라스틱의 98%는 화석연료로부터 생산되기 때문에 생산과정에서 다량의 탄소를 배출하게 되고, 플라스틱 폐기는 주로 매립, 소각의 방식으로 처리되기 때문에 폐기 과정에서도 탄소를 배출하게 된다. 또한, 재활용은 극히 미미할 뿐만 아니라, 수집-운반-선별-가공의 복잡한 단계를 거치는 과정에서 대량 유실이 발생한다. 일반 석유계 플라스틱은 미생물 분해가 불가능한 화학 구조를 가지고 있기 때문에 자연분해 시 500년 이상이 소요된다.
따라서, 자연분해가 가능한 제품을 생산하는 것이 플라스틱으로 인한 환경 문제를 해결할 수 있는 방안일 것이다. 이에 대해 정부는 폐플라스틱 발생량 감축을 목표로 하고 있으며, 각 화학업체에서도 플라스틱 규제에 대해 다양한 방안을 마련하고 있다.
지속적인 플라스틱 수요 증가로 생산 감축은 어려우며, 플라스틱 재활용도 최종적으로는 폐기물을 남길 수밖에 없는 점을 고려하면 생분해가 가능한 플라스틱을 사용하는 것이 근본적인 해결책이다. 바이오 플라스틱 생산량은 연평균 20% 이상의 고성장을 이루고 있으며, 바이오 플라스틱 중에서도 생분해성 플라스틱인 PLA가 압도적으로 큰 시장 규모를 형성하고 있다. polylactic acid(PLA)는 우수한 기계적 특성과 생체 적합성, 투명성을 가진 생분해성 고분자이지만, 고유한 취성(brittleness)과 낮은 충격강도로 인해 다양한 분야에서의 적용을 크게 제한한다.1 따라서 polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT), polycaprolactone(PCL), poly butylene succinate(PBS)와 같은 유연한 생분해성 고분자와 블랜드하여, PLA의 인성을 개선한다. 이 중 PBAT는 높은 파단 신율, 우수한 가공특성을 가지고 있는 유연한 생분해성 고분자로 PLA의 인성을 향상시키는데 주로 사용한다. 또한, PLA에 나노 필러를 첨가하여 기계적 특성을 개선하고, 전기적 특성을 부여할 수 있다.
전도성을 부여하는 탄소계 필러로는 카본블랙(carbon black, CB), 탄소섬유(carbon fiber, CF), 탄소나노튜브(carbon nano tube, CNT)가 있으며, 이 중 CNT는 큰 종횡비와 경도 때문에 나노 필러로 널리 사용된다.1 전도성 고분자 복합소재는 주로 열가소성 고분자에 전도성 필러를 첨가하여 제조할 수 있으며, 고분자 블랜드에 나노 입자를 첨가하면 우수한 기계적, 전기적 특성을 가진 복합재료 제조가 가능하다.
전도성 복합소재 제조 시, 필러의 농도가 낮으면 고분자 블랜드 내에서 필러는 서로 닿지 않아 비전도성을 나타내고, 필러의 농도가 어느 임계 함량으로 증가하면 전기전도도가 급격하게 증가하게 된다. 이 현상이 발생하는 농도를 전기적 침투 임계 함량이라고 하며, 이 이상에서 재료는 전기전도성으로 간주한다.2 높은 전기전도성을 가지는 소재를 제조하기 위해서는 많은 양의 필러 첨가가 필수적인데 과량의 필러는 소재의 단가를 증가시키며, 가공성과 기계적 성능을 저하시킨다. 이러한 이유로 소재 내 CNT를 잘 분산시켜, 전기적 침투 임계 함량(electrical percolation threshold)을 줄이는 것이 가장 중요하다. 전기적 침투 임계 함량을 줄이는 혁신적인 방법은 이중 침투(double percolation)이다.3 Double percolation은 혼합되지 않는 2상 블랜드를 복합재의 매트릭스로 사용하여, 공연속(co-continuous) 구조를 형성시키고 필러를 한 상 또는 계면에 위치하게 하는 것이다.4
따라서, 본 연구에서는 PLA의 취성을 개선하기 위해 PBAT를 블랜드하여 내충격성이 우수한 PLA/PBAT 블랜드를 제조하고, CNT를 첨가하여 전기전도성이 부여된 친환경 전도성 고분자 복합소재를 제조한다. 나아가 혼합 공정 최적화, PLA/PBAT 상용성 개선을 통해 CNT의 분산을 개선하여 최소 함량의 필러로 전기전도성이 향상된 고성능 생분해성 복합소재를 제조하고자 한다. 제조한 생분해성 복합소재는 전자파 차폐, 대전 방지, 정전기 방지 재료로 활용이 가능하며, 나아가 생체 센서, 롤러블 디스플레이, 웨어러블 전자기기 등에도 활용이 가능할 것이라 기대한다.
재료. PLA(IngeoTM Biopolymer 3251D)는 NatureWorks Co. Ltd.(USA)의 제품을 구매하였다. PLA의 물성은 다음과 같다. Specific gravity는 1.24, 유리전이온도는 55-60 ℃, 용융 온도는 155-170 ℃, melt flow index(190 ℃, 2.16 kg)는 35 g/10 min 이다. PBAT(A400)는 ZhuHai WanGo Chemical Co., Ltd.(China)의 제품을 구매하여 사용하였으며, PBAT의 물성은 Specific Gravity는 1.22, 용융 온도는 115-125 ℃, melt flow index(190 ℃, 2.16 kg)는 4.0 g/10 min이다. MWCNT(K-Nanos 210)는 금호석유화학(주)(Korea) 제품을 구매하였다. MWCNT는 다발 길이 40-50 um, 직경 11-13 nm, 순도는 95% 이상의 pellet type을 사용하였다. 상용화제는 BASF SE(Germany)사의 Joncryl® ADR 4468을 사용하였다. ADR 4468의 specific gravity, 25 ℃는 1.08, 분자량은 7250, 유리전이온도는 95 ℃, 에폭시 당량은 310 g/mol이다.
블랜드 제조. 실험 전, PLA와 PBAT는 수분에 의한 물성 저하를 방지하기 위해 80 ℃ 진공 오븐에서 24시간 동안 건조하였다. PLA/PBAT 기반 전도성 나노복합재는 torque rheometer (Thermo ScientificTM HAAKE PolyLab OS batch mixer, HAAKE, Germany)를 사용하여 제조하였다. 가공 조건은 온도 180 ℃, 스크류 속도는 60 rpm, 혼련시간은 총 8분이다.
유변학적 특성. 유변학적 특성은 회전형 레오미터(Anton Paar MCR 102, Austria) 25 mm plate-plate로 진행되었다. Dynamic frequency sweep test는 180 ℃에서 진행되었으며, strain 1%에서 0.1-100 rad/s angular frequency sweep test(ω)를 진행하였다. 폴리머의 선형 점탄성 구간을 결정하기 위해 strain sweep test는 가장 먼저 수행하였다.
모폴로지 특성. 모폴로지 특성은 전자주사현미경(SEM IM-60, ISP, Korea)으로 확인하였다. 샘플은 액화 질소에서 30분 동안 냉각한 뒤 파단하였으며, 스퍼터링 장치를 사용하여 금 코팅을 하였다. 10 kV의 가속전압에서 샘플의 파단면을 관찰하였다.
전기적 특성.체적저항은 volume resistivity tester(2450 Source Meter®, SMU Instrument)로 측정하였다. 저항률은 상온에서 측정하였으며, 2단자법으로 10회 측정하였다.
기계적 특성. 인장강도는 universal testing machine DTU-900MHA(UTM, Daekyung tech.)으로 상온에서 측정하였다. 인장강도의 시편은 hot press molding을 사용하여 ASTM D638의 규격으로 제작하였으며, crosshead speed는 10 mm/min으로 5회 진행하였다. 충격강도는 IZOD impact tester (DTI-602, Daekyung tech)로 상온에서 측정하였다. 시편은 hot press molding을 사용하여 ASTM D256의 규격으로 제작하였으며, 10회 진행하였다.
열적 특성. 시차 주사 열량계를(DSC, Q20 TA instruments, USA) 사용하여 측정하였다. DSC cell을 50 mL/min의 유속의 질소 분위기에서 4 mg의 샘플을 알루미늄 팬에 넣어 측정하였다. DSC는 1차 가열-1차 냉각-2차 가열의 과정을 거쳐 진행하였다.
CNT 함량 최적화. 생분해성 PLA/PBAT 블랜드의 CNT 침투 임계 함량을 확인하고, 최적화하기 위한 실험을 수행하였다.수지 및 첨가제의 함량은 Table 1에 표기하였다.
제조한 블랜드의 유변학적 특성 평가 결과, CNT 함량이 증가함에 따라 저장탄성률(storage modulus)과 복소점도(complex viscosity)는 증가하였다. 저장탄성률의 증가는 강도가 높은 CNT의 강화 효과로 인해 나타나는 결과이며, 복소점도의 증가는 CNT가 PLA와 PBAT의 사슬 이동성을 감소시켰기 때문이다.5 Figure 1(a)에서 CNT의 함량이 2 phr 이상일 때, 낮은 주파수 영역에서 저장탄성률의 기울기가 평탄해지면서 재료는 탄성체와 같은 거동을 보임을 확인할 수 있다. Figure 1(b)에서는 CNT의 함량이 2 phr 이상일 때, 낮은 주파수 영역에서 점도 기울기가 급격하게 증가하는 것을 볼 수 있다. Figure 1(c)에서 tan delta 값이 1보다 크면 점성체, 1보다 작으면 탄성체와 같은 거동을 하는 것이라 해석할 수 있다. 유변학적 침투 임계 함량(rheological percolation threshold)은 재료가 점성체와 같은 거동에서 탄성체와 같은 거동으로 변하는 하는 지점을 의미한다.6 제조한 블랜드는 CNT의 함량이 증가함에 따라 탄성체와 같은 거동을 보이며, 특히 CNT2에서 재료가 점성체와 같은 거동에서 탄성체와 같은 거동으로 변하는 것을 확인하였다. 따라서, 유변학적 침투 임계 함량은 CNT 2 phr임을 알 수 있다.
CNT 첨가 및 함량 증가에 따른 블랜드의 구조를 확인하기 위해 주사전자현미경(SEM)으로 시료의 파단면을 관찰하였다. SEM 이미지에서 매트릭스 상은 PLA, 분산 상은 PBAT이다. 어떠한 첨가제도 넣지 않은 Figure 2(a)는 두 폴리머 사이의 비상용성으로 인해 바다-섬(sea-island) 구조를 나타낸다. 또한, 계면이 명확하게 관찰된다. PLA/PBAT 블랜드에 CNT 1 phr을 첨가하면 분산 상의 크기가 불규칙적으로 변하지만, 여전히 바다-섬 구조를 보이며 계면이 명확하게 관찰된다. 그러나 CNT 함량이 2 phr 이상일 때, 분산 상의 크기가 증가하는 것을 볼 수 있다. CNT는 지방족 사슬을 가지고 있는 PLA보다는 방향족 사슬을 가지고 있는 PBAT와 화학적 친화도가 높은 것으로 알려져 있다.7 이러한 이유로 PLA/PBAT 블랜드에서 CNT는 PBAT 상에 주로 위치하기 때문에 분산 상의 크기가 증가하게 되는 것이다.8 이후 2 phr 이상의 함량에서는 두 고분자의 계면이 거의 관찰되지 않는다. 그 이유는 다음과 같이 설명할 수 있다. 고분자 블랜드에 나노 입자를 첨가하는 경우, 나노 입자는 두 고분자 중 한 상 또는 두 고분자 계면에 존재하게 된다. PLA/PBAT에 CNT를 첨가하게 되면 화학적 친화도로 인해 PBAT 상에 주로 하게 되나, 많은 양의 CNT를 첨가하게 되면 제한된 PBAT의 함량으로 인해 CNT가 두 고분자 계면에 위치하게 된다. 따라서, PLA/PBAT의 상용성을 증가시켰기 때문에 두 고분자의 계면 접착력이 증가한 것이다.
블랜드의 열적 특성을 확인하기 위해 시차주사열량계(DSC)를 사용하였다. Table 2는 PLA/PBAT 블랜드의 유리전이온도, 냉결정화 온도, 용융 온도는 PLA 수지의 특성을 나타내는 것을 알 수 있다. 제조된 블랜드에서 CNT의 함량이 증가함에 따라 유리전이온도, 냉결정화 온도는 감소한다. 비상용성의 고분자를 블랜드하는 경우, 유리전이온도는 주로 함량이 높은 고분자에 의해 결정된다. 그러나 두 고분자의 친화성이 증가하면, 블랜드의 유리전이온도는 두 고분자의 유리전이온도 사이 값을 나타낸다. 이러한 이유로, PLA/PBAT에 CNT 함량이 증가함에 따라 PLA 유리전이온도가 낮아지고 있어, 즉 두 고분자의 상용성이 증가하는 것이라 판단할 수 있다. 이는 SEM에서 살펴본 모폴로지 분석 결과와도 일치하는 결과이다. 추가적으로, CNT 함량이 증가함에 따라 냉결정화 피크가 약해지는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 결정화 엔탈피가 감소하는 것이며, 이를 통해서는 CNT의 존재가 결정화를 방해하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 또한, CNT 함량이 증가함에 따라 블랜드 내에 나노 입자의 양이 증가하게 되고, 이로 인해 결정 생성에도 더 많은 방해가 되어 결정화 능력이 약해짐을 의미한다.
제조한 블랜드의 전기적 특성을 확인해보기 위해 체적저항률을 측정하였다. 체적저항률은 주어진 순수한 물질의 고유저항으로, 측정 표면의 저항과 면적 그리고 물체의 두께를 고려한 값이다. 일반적으로 체적저항이 높을수록 재료는 절연체, 낮을수록 도체의 성질을 가지게 된다. 고분자 재료에서 체적저항률이 103-104 W·cm 이하인 경우, 전기전도성이 부여된 전도성 재료로 간주한다.
Figure 3에서 PLA, PLA/PBAT는 절연체의 체적저항률을 보인다. 일반적으로 고분자 소재는 전기 절연성의 특징을 가지기 때문에 높은 체적저항률을 가진다. 전기적 특성을 부여하기 위해 PLA/PBAT 블랜드에 CNT 1 phr을 첨가하여도, 여전히 절연체의 특성을 보인다. 그러나, CNT 2 phr 이상부터 체적저항률이 도체 영역의 값을 보이면서 급격하게 감소한다. 이는 고분자 블랜드 안에서 CNT가 서로 닿아 전도성 네크워크를 형성하였기 때문에 체적저항이 감소하는 것이다. 이렇게 블랜드 내에 필러의 농도가 어느 임계 함량으로 증가하면 전기전도도가 급격하게 증가하는데, 이 현상이 발생하는 농도를 전기적 침투 임계 함량(electrical percolation threshold)이라고 하며, 이 이상에서 재료는 전도성으로 간주한다. 그렇기 때문에, PLA/PBAT의 전기적 침투 임계 함량은 CNT 2 phr임을 알 수 있다.
제조한 블랜드의 기계적 특성 중, 충격강도는 Figure 4에 나타내었다. 충격강도는 재료가 파괴되는데 필요한 에너지를 단위 면적이나 단위 폭에 대해 나타낸 값으로, 충격강도가 높을수록 내충격성이 우수한 재료를 의미한다. 충격강도 측정 결과, PLA는 취성으로 인해 충격강도가 가장 낮다. 그러나, 취성(brittleness)이 높은 PLA에 연성(ductility)이 높은 PBAT를 블랜드하면, PLA의 취성이 보완되어 충격강도가 증가하게 된다. 한편, CNT를 첨가하는 경우엔 CNT 함량이 증가함에 따라 충격강도가 증가하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 CNT가 고강도 탄소섬유이기 때문에, 함량이 증가함에 따라 기계적 물성이 향상되는 것이다. 또한, Figure 2에 나타난 SEM 결과와 같이 높은 함량의 CNT가 첨가되면, 필러가 PLA/PBAT 계면에 위치하여 두 고분자의 상용성을 개선하기 때문에 기계적 물성이 증가하는 것이다.
혼합 공정 최적화. 혼합 공정을 최적화하기 위해, 다양한 혼합방법으로 블랜드를 제조하였으며, 혼합방법과 함량은 Table 3에 나타내었다. CNT 함량은 예비 실험을 통해 확인한 2 phr로 고정하였다.
Pr1은 고분자 수지와 첨가제를 일괄투입방식으로 제조한 블랜드이다. Pr2과 Pr3는 각각 PLA 또는 PBAT와 CNT를 먼저 혼합한 뒤, PBAT 또는 PLA를 첨가하는 방식으로 제조하였고, Pr4는 PLA와 PBAT를 사전용융 혼합한 뒤, CNT를 첨가하는 방식으로 제조하였다. 다양한 혼합방법으로 제조한 블랜드 내의 CNT의 분산을 평가하기 위해 유변학적 물성을 측정하였고, 그 결과는 Figure 5에 나타내었다. Figure 5에서 저장탄성률과 복소점도 모두 PLA와 PBAT를 사전용융 혼합한 뒤, CNT를 첨가하는 방식으로 제조한 Pr4가 가장 높은 유변물성을 보였다. Pr4는 용융상태인 PLA/PBAT에 CNT가 첨가되었기 때문에, 두 고분자의 용융온도 차이에 의한 영향을 제거할 수 있다. 이러한 이유로, CNT의 입자 이동성이 향상되어 두 고분자에 잘 분산되어 응집체가 형성되지 않았기 때문에 더욱 안정적인 구조를 형성했을 것이라 판단된다. 또한, Internal batch mixer로 CNT를 첨가하여 고분자와 용융 혼합하는 경우, 스크류가 회전하는 전단력에 의해 CNT가 고분자 용융체에 분산된다. Pr1과 Pr4의 경우, Step 1에서 CNT와 두 수지를 모두 첨가하여 믹서 내 챔버 부피를 70%로 채운 다음 블랜드를 제조하는 반면에 Pr2과 Pr3의 경우, 각각 60%, 25%만 채워진 상태에서 블랜드가 제조된다. 따라서 모든 블랜
드가 동일한 전단력을 받지 못했기 때문에 CNT의 분산에 영향을 주었을 것이다. 따라서, Internal batch mixer로 전도성 복합소재 제조 시 고분자 매트릭스는 믹서 내부 챔버 부피를 70% 이상으로 채워 전단력에 의한 분산을 향상시키고, 용융상태의 고분자 블랜드에 나노 필러를 혼합하는 것이 가장 최적 혼합 공정임을 확인하였다.
상용성 개선을 통한 전도성 복합재 제조. PLA/PBAT 상용성 개선을 통해 CNT의 분산을 개선하고자 에폭시 링을 함유하고 있는 상용화제 ADR 4468 투입을 결정하였다. 블랜드 제조 시, 수지를 총 3단계에 거쳐 믹서에 투입하였다. 각 단계에서 수지는 일괄투입 되었으며, 블랜드 조성 및 첨가제의 함량은 Table 4에 나타내었다. 제조 과정에서 PLA/PBAT 매트릭스를 사전 용융한 경우, 샘플 이름에 _P를 기재하였다.
CNT의 분산상태를 조사하고, 제조한 복합소재의 미세구조를 예측하기 위해 동적 유변물성 테스트를 수행하였다.5 유변학적 분석에서 저장탄성률의 저주파수 영역은 고분자 블랜드의 미세구조에 관한 정보를 얻을 수 있는 구간이다. Figure 6는 PLA/PBAT 기반 복합소재의 저장탄성률, 복소점도의 주파수 의존성을 나타낸다. Figure 6에서 PLA/PBAT 블랜드에 CNT를 첨가하게 되면 저장탄성률과 복소점도는 급격히 증가한다. 특히 복소점도의 경우 나노 필러를 첨가하게 되면 전단박화 거동(shear thinning)거동을 보이는데, 이는 고분자 블랜드 내 높은 함량의 나노입자 첨가 및 가교 구조에 의해 분자량이 증가했을 경우 나타나는 현상이다.9 상용화제를 첨가한 경우엔 고주파수 영역에서는 더 높은 물성을 보였으나 저주파수 영역에서는 큰 차이가 나타나지 않았다. 고주파수 영역에서 더 높은 물성을 보인 이유는 상용화제인 ADR이 PLA와 PBAT 말단에 존재하는 카르복실기 또는 하이드록시기와 반응하면서 두 고분자의 상용성을 증가시켰기 때문이다.10 그러나, 고분자 매트릭스를 사전에 용융 혼합한 뒤 ADR를 첨가하게 되면 일괄 투입하여 제조한 블랜드에 비해 같은 CNT 함량임에도 더 높은 유변물성을 보이는 것을 확인하였다. 또한, 저주파수 영역에서 저장탄성률의 기울기가 평탄한 영역이 길어지는 것을 확인하였다. 저주파수 영역에서 저장탄성률의 기울기가 평탄한 영역이 길어진 것은 블랜드 내에 나노 필러가 잘 분산되어 안정적인 3D-network 구조를 형성했다는 것을 의미한다.8 따라서 복합소재는 탄성체와 같은 거동을 하게 된다. 이를 통해 상용화제 첨가보단 고분자 매트릭스의 사전용융 혼합 여부가 CNT 분산 및 안정적인 3D-network 구조 형성에 더 큰 영향을 미치는 것이라고 판단하였다.
유변학 분석에서 Tan delta 그래프와 Cole-cole 그래프는 고분자 블랜드의 미세구조를 예측할 수 있는 지표로 활용된다.11 Figure 6(c)에서 저주파수 영역의 저장탄성률은 일괄투입 블랜드에 비해 고분자 매트릭스를 사전 용융혼합 한 경우 더욱 탄성체와 같은 거동을 보인다. 특히, CNT_P가 가장 탄성체와 같은 거동을 보인다. Figure 6(d)에서도 PLA/PBAT를 제외한 나머지 블랜드에서 같은 함량의 CNT가 첨가되었음에도 불구하고 그래프는 모두 다른 영역에서 나타난다. 이를 통해 고분자 미세구조에 변화가 발생했을 것이라 판단된다.12 따라서, CNT와 ADR의 첨가, 그리고 고분자 매트릭스 사전용융 혼합 여부에 의해 블랜드의 미세 구조가 변하였음을 확인하였다. 또한, CNT_P 가장 안정적인 3D-network 구조를 형성하였음을 알 수 있다.
CNT 위치 및 고분자 블랜드의 구조를 확인하기 위해 SEM을 사용하여 고분자 블랜드의 파단면을 관찰하였다. Figure 7에서 CNT 단독 첨가 블랜드 대비 상용화제를 함께 첨가하게 되면 분산 상의 크기가 작아지는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이는 상용화제인 ADR의 첨가로 인해, 두 고분자의 상용성이 증가하여 분산상의 크기가 작아지는 것이다.
한편, SEM 이미지를 통해서도 고분자 매트릭스 사전용융 혼합 여부에 따른 차이를 관찰할 수 있다. 고분자 매트릭스와 첨가제를 일괄 투입한 Figure 7(a)과 Figure 7(c)에서는 두 고분자 사이의 계면이 뚜렷하게 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 또한, CNT가 잘 분산되지 않아 분산 상에 응집되어 존재하게 된다. 그러나 고분자 매트릭스를 사전 용융 혼합한 Figure 7(b)과 Figure 7(d)에서는 두 고분자 사이의 계면 접착력이 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있으며, CNT가 응집되어 있는 형태도 거의 관찰되지 않는다. 특히, Figure 7(b)의 경우, 바다-섬 구조에서 공연속 구조로 구조적 변화가 발생하여 double percolation 달성에 유리함을 알 수 있다. 이러한 형태를 보이는 이유는 다음과 같이 설명할 수 있다. 두 고분자와 첨가제를 일괄 투입하여 복합소재를 제조하면 용융온도가 낮은 PBAT와 CNT가 먼저 혼합되고, 이후 PLA가 용융상태가 되어도 화학적 친화도로 인해 CNT는 PBAT 상에만 국한되기 때문에, PLA 상 또는 두 폴리머 사이의 계면으로 분산되지 않는다. 따라서 두 고분자 사이의 약한 계면 접착력과 CNT 응집체가 관찰되는 것이다. 하지만 고분자 매트릭스를 사전 용융 혼합하여 복합소재를 제조하면 두 고분자의 용융온도 차이에 의한 영향이 제거되기 때문에, CNT는 두 고분자와 계면 모두에 잘 분산되어 강한 계면 접착력을 보이고, CNT의 응집체는 관찰되지 않는 것이다. 또한, 폴리머 매트릭스가 용융상태가 된다면 점도가 감소하여 나노 필러의 이동성 향상으로 CNT의 분산이 개선되는 것이다.
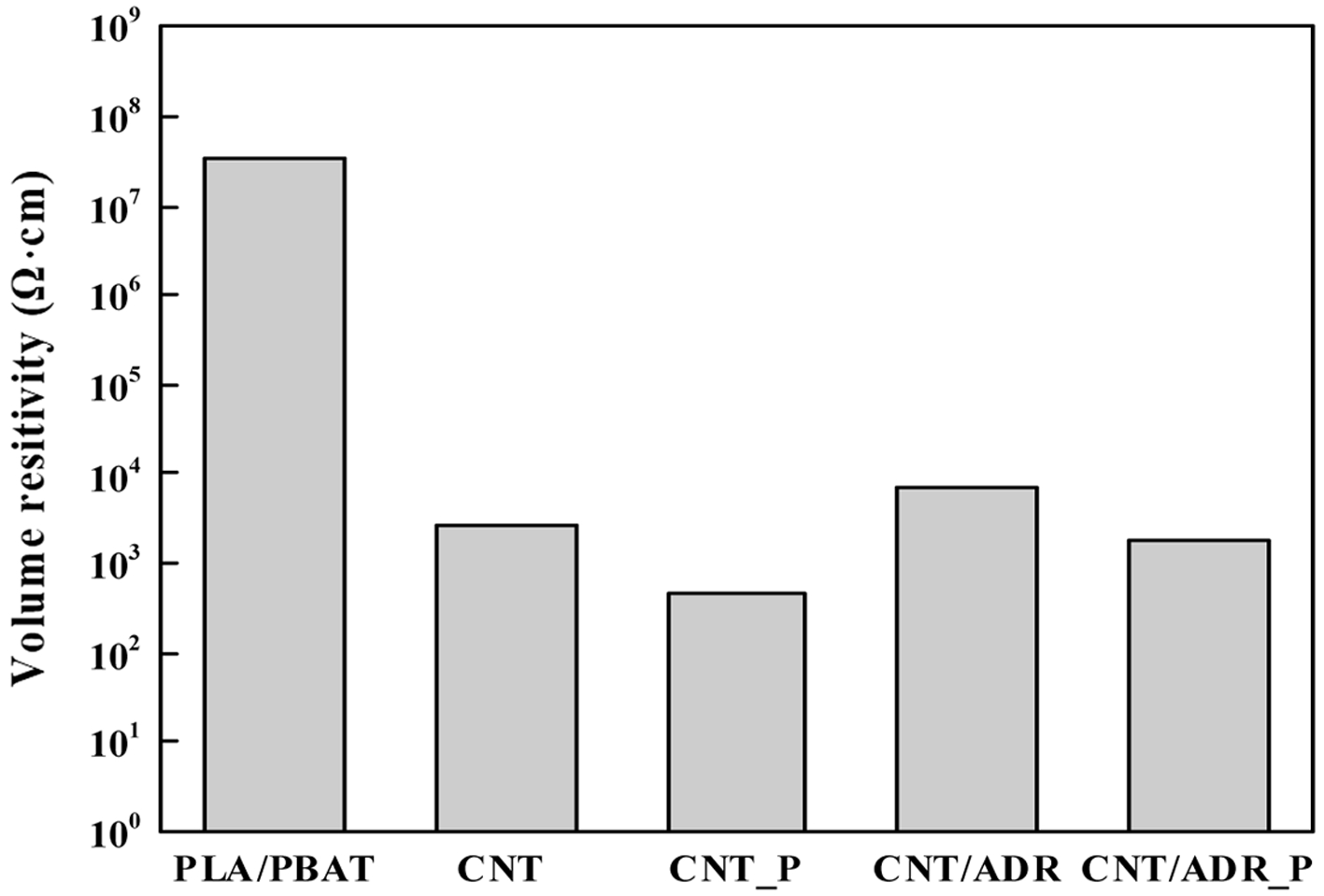
제조한 복합소재의 전기적 특성을 조사한 결과 PLA/PBAT를 제외한 블랜드는 모두 도체 영역의 체적저항률을 보이나, 동일한 함량의 CNT가 첨가되었음에도 불구하고 모두 다른 체적저항률을 보이게 된다(Figure 8). 이를 통해, 상용화제 첨가 또는 고분자 매트릭스 사전용융 혼합 여부가 CNT의 분산이나 고분자 블랜드의 구조적 변화를 초래하여 전도성 경로 형성에 영향을 주었다고 판단할 수 있다. 제조한 블랜드 중 체적저항률이 가장 낮은 샘플은 CNT_P이다. 이는 유변학적 물성 분석 결과와도 일치하는 결과이며, double percolation 이론에 의해 CNT가 두 고분자 계면에 주로 위치하고 공연속 구조를 형성한 CNT_P가 가장 높은 전기적 특성을 나타내게 되는 것이다. 이에 반해 ADR을 첨가하는 경우, 상용성 개선으로 분산 상의 크기가 작아지게 되면서 공연속 구조 형성에 방해가 되어 오히려 체적저항률이 약간 증가함을 볼 수 있다. 이를 통해, 전도성 네트워크을 형성하기 위해서는 비상용성 고분자 매트릭스의 상용성 개선보다도 CNT의 위치와 공연속 구조 형성이 더 중요한 요소임을 확인하였다.
CNT와 상용화제인 ADR이 PLA/PBAT 기반 복합소재의 기계적 특성에 미치는 영향은 Figure 9에 나타내었다. 고분자 블랜드에서 두 수지 간의 비상용성은 물성 저하를 초래한다. PLA/PBAT 블랜드의 경우, 두 고분자 사이에 낮은 호환성과 계면 접착력으로 가장 낮은 기계적 물성을 보인다. PLA/PBAT 블랜드에 CNT를 첨가하게 되면 고강도 CNT의 강화 효과로 인하여 기계적 물성이 약간 증가하게 된다. 특히, CNT와 ADR을 모두 첨가하면 파단 연신율, 강인성, 충격강도는 1.5~2배 이상 증가한다. 이는 높은 연성을 가지는 PBAT와 PLA의 상용성 증가와 고강도 섬유의 강화 효과 때문에 나타나는 결과이다.13 유변학적 특성 분석 결과 ADR을 첨가하면 PLA-PBAT 공중합체가 형성되어 점도가 크게 증가한다. 또한, 모폴로지 특성 분석 결과 ADR을 첨가하는 경우 상용성 증가로 인해 분산 상의 크기가 감소하였다. 이를 통해 기계적 특성의 결과를 뒷받침할 수 있다. 결론적으로, ADR 첨가로 PLA와 PBAT의 상용성이 증가하여 PLA의 취성이 개선되고, 재료의 내충격성이 향상됨을 알 수 있다.13
기계적 물성에서도 고분자 매트릭스 사전용융 혼합여부에 대한 영향을 확인할 수 있다. 일괄투입으로 제작한 블랜드에 비해 고분자 매트릭스를 사전용융 혼합한 블랜드의 경우, 더 높은 기계적 물성을 보인다. 이는 CNT가 주로 계면에 위치하여 두 고분자 간의 계면 접착력을 증가시켰기 때문이다. 따라서 고분자-고분자 계면에 위치한 CNT가 응력을 전달하고, 응력 집중으로 인한 파손을 줄일 수 있어 높은 기계적 물성을 가지게 된다.1 또한, 모든 기계적 물성이 증가한 이유는 CNT가 고강도 필러로 작용함과 동시에 PLA/PBAT의 상용성을 개선하였기 때문이라 판단된다. 해당 결과로 CNT의 위치 최적화 및 고분자 매트릭스의 상용성 증가가 높은 기계적 물성을 달성하는데 유리한 것을 확인하였다.

|
Figure 1 Dynamic Frequency Sweep Tests of biodegradable PLA/ PBAT blend with CNT: (a) storage modulus; (b) complex viscosity; (c) tan delta. |

|
Figure 2 SEM images of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend with CNT: (a) PLA/PBAT; (b) CNT1; (c) CNT2; (d) CNT3; (e) CNT4; (f) CNT5. |

|
Figure 3 Volume resistivity of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend with CNT. |

|
Figure 4 Notch impact strength of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend with CNT. |

|
Figure 5 Dynamic frequency sweep tests of the blend manufactured for mixing process optimization: (a) storage modulus; (b) complex viscosity. |

|
Figure 6 Dynamic frequency sweep tests of PLA/PBAT-based conductive composites through improved compatibility: (a) storage modulus; (b) complex viscosity; (c) cole-cole plot; (d) tan delta. |

|
Figure 7 SEM images of PLA/PBAT-based conductive composites through improved compatibility: (a) CNT; (b) CNT_P; (c) CNT/ ADR; (d) CNT/ADR_P. |

|
Figure 8 Volume resistivity of PLA/PBAT-based conductive composites through improved compatibility. |

|
Figure 9 Mechanical properties of PLA/PBAT-based conductive composites through improved compatibility: (a) tensile strength; (b) elongation at break; (c) toughness; (d) notch impact strength. |
|
Table 3 Mixing Methods and Contents of the Blend Manufactured for Mixing Process Optimization |

|
Table 4 Mixing Methods and Contents of Conductive Composites for Improved Compatibility |

- 1. Zhao, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Strong Synergistic Toughening and Compatibilization Enhancement of Carbon Nanotubes and Multi-Functional Epoxy Compatibilizer in High Toughened Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) Blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126204.
-

- 2. Liu, Y.; He, H.; He, G.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Tian, G. Segregated Polylactide/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/MWCNTs Nanocomposites with Excellent Electrical Conductivity and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e51668.
-

- 3. Strugova, D.; David, É.; Demarquette, N. R. Electrically Conductive Polymer Composites. LEPAC – Lab. Eng. Polym. Compos. 2023, Feb 1.
- 4. Sumita, M.; Sakata, K.; Asai, S. Dispersion of Fillers and the Electrical Conductivity of Polymer Blends Filled with Carbon Black. Polym. Bull. 1991, 25, 265-271.
-

- 5. Zeng, Q.; Du, Z.; Qin, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Enhanced Thermal, Mechanical and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of Graphene Nanoplatelets-Reinforced Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(ethylene oxide) Nanocomposites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101632.
-

- 6. Penu, C.; Hu, G.-H.; Fernandez, A.; Marchal, P.; Choplin, L. Rheological and Electrical Percolation Thresholds of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 2173-2181.
-

- 7. Ko, S. W.; Gupta, R. K.; Bhattacharya, S. N. Rheology and Physical Characteristics of Synthetic Biodegradable Aliphatic Polymer Blends Dispersed with MWNTs. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 320-328.
-

- 8. Dil, E.; Otero, I.; Sundararaj, U.; Favis, B. Interface Bridging of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Polylactic Acid/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): Morphology, Rheology, and Electrical Conductivity. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 10267-10277.
-

- 9. Ko, S.; Hong, M.; Park, B.-J.; Gupta, R.; Choi, H.; Bhattacharya, S. Morphological and Rheological Characterization of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/PLA/PBAT Blend Nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 2009, 63, 125-134.
-

- 10. Liliane Cardoso Arruda, Marina Magaton, RosaArruda, L. C.; Magaton, M.; Bretas, R. E. S.; Ueki, M. M. Influence of Chain Extender on Mechanical, Thermal and Morphological Properties of Blown Films of PLA/PBAT Blends. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 27-37.
-

- 11. Wu, D.; Huang, A.; Fan, J.; Xu, R.; Liu, P.; Li, G.; Yang, S. Effect of Blending Procedures and Reactive Compatibilizers on the Properties of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/Poly(lactic acid) Blends. J. Polym. Eng. 2021, 41, 95-108.
-

- 12. Xiao, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Lin, J. The Carbon Nanotubes Effects on the Morphology and Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 27053.
-

- 13. Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X. Mechanical Properties, Rheological Behaviors, and Phase Morphologies of High-Toughness PLA/PBAT Blends by In-situ Reactive Compatibilization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 107028.
-

- Polymer(Korea) 폴리머
- Frequency : Bimonthly(odd)
ISSN 2234-8077(Online)
Abbr. Polym. Korea - 2024 Impact Factor : 0.6
- Indexed in SCIE
 This Article
This Article
-
2026; 50(1): 151-160
Published online Jan 25, 2026
- 10.7317/pk.2026.50.1.151
- Received on Sep 2, 2025
- Revised on Oct 1, 2025
- Accepted on Oct 1, 2025
 Services
Services
Shared
 Correspondence to
Correspondence to
- Dong Hak Kim
-
Department of Chemical Engineering, Soonchunhyang University, Asan-si, Chungcheongnam-do, 31538, Korea
- E-mail: dhkim@sch.ac.kr
- ORCID:
0009-0007-5932-2943











 Copyright(c) The Polymer Society of Korea. All right reserved.
Copyright(c) The Polymer Society of Korea. All right reserved.